
Implementation of the electronic invoicing system in the UAE: from paper trails to real-time oversight
October 2025
On 29 September, the UAE Ministry of Finance issued Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 on the Electronic Invoicing System and Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 on the Implementation of the Electronic Invoicing System, for the purpose of establishing the scope of application of the Electronic Invoicing System and the obligations of the persons subject to it. The goal of these measures is to align the UAE with international e-invoicing standards and strengthen tax compliance, transparency and digital transformation across the public and private sectors.
An electronic Invoice is an invoice issued, transmitted and received in a structured electronic format that enables automatic and electronic processing. Unlike traditional invoices (PDFs, Word documents, or scanned images), e-invoices must be issued in structured digital formats (XML), transmitted via an Accredited Service Provider through the Peppol-based DCTCE (Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control and Exchange / 5 corner) model and reported to the Federal Tax Authority’s (FTA) for validation and compliance monitoring.
Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 on the Electronic Invoicing System defines the system’s scope and obligations:
- Applies to all B2B and B2G transactions conducted in the UAE, except for specific exclusions such as government activities in a sovereign capacity and certain airline services, which fall outside the scope of the e-invoicing requirements;
- B2C transactions are currently excluded from mandatory implementation;
- Companies must issue and transmit electronic invoices and credit notes within 14 days from the date of business transaction;
- Businesses must use an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) to manage the issuance, transmission and receipt of all invoices and credit notes.
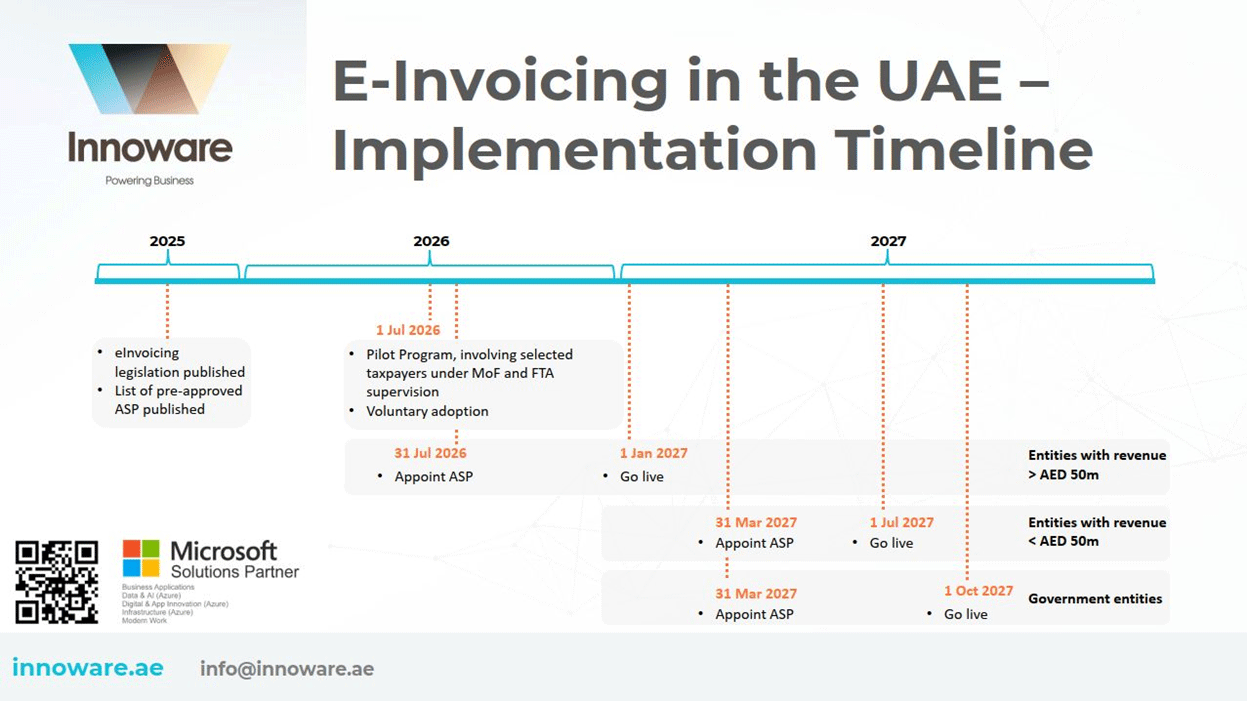
Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 on the Implementation of the Electronic Invoicing System sets the implementation phases:
- By July 2026, the UAE will launch a pilot e-Invoicing program. A selected group of taxpayers (Taxpayer Working Group) under the supervision of the Ministry of Finance and FTA will participate in testing the system. Companies can voluntarily join the pilot project or start early implementation from July 2026;
- Entities with revenues of AED 50 million or more must appoint an ASP by 31 July 2026 and go live by 1 January 2027. Businesses with revenues below AED 50 million and government entities must appoint an ASP by 31 March 2027, with go-live dates of 1 July 2027 for businesses and 1 October 2027 for government entities;
- B2C transactions remain exempt from mandatory implementation until a separate ministerial decision includes them into scope.
How can businesses prepare?
For companies, this change makes it essential to ensure that their current ERP system is compatible with e-invoicing standards. Many organizations are beginning to realize that their ERP solution is either outdated or not flexible enough to seamlessly integrate e-invoicing.
To check ERP readiness, companies should review whether their system can:
- Generate invoices in a structured XML format as required by the FTA;
- Include all mandatory data fields (supplier and buyer details, TRN, VAT amounts, invoice type, timestamps, etc.);
- Automate invoice signing and validation to ensure compliance with FTA standards;
- Maintain accurate master data (TRN, legal name, address, VAT treatment);
- Provide real-time error tracking and audit trail visibility;
- Identify and eliminate any manual steps still involved in the invoicing or approval process.
Preparing for the implementation of e-invoicing requires careful planning. Organizations need to review data, configure their system to comply with the new requirements and conduct preliminary testing. For this reason, preparation should begin well in advance of the mandatory implementation deadline.
If you would like to receive a consultation on how to prepare your business for e-invoicing implementation, learn more about Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP solutions that are fully compatible with the e-invoicing standard, or calculate the cost of an ERP implementation project specifically for your company, contact Innoware specialists by phone: +971588894591 or email: info@innoware.ae.
INNOWARE USA
501 Silverside Rd, Ste 105, # 4995,
Wilmington, Delaware, 19809-1376,
United States
Tel.: +1(302)4672024
E-mail: info@innoware.com
INNOWARE UAE
Premises 407-FZBA 055, 4th Floor, Sheikh Rashid Tower, Dubai World Trade Centre,
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel.: +971588894591
E-mail: info@innoware.ae
INNOWARE UKRAINE
3, Sholudenka St., office 204 (Cubic BC)
Kyiv, Ukraine, 04116
Tel.: +380(44)4902220
E-mail: info@innoware.com


